Gas Furnace Equipment Components and How They are Utilized
There are many different parts that keep your furnace operating smoothly and efficiently. Below we will be breaking down the individual parts of your furnace system. We are going to be focusing on gas powered furnace components and non-geothermal heating methods. We are not going to be focusing as much on furnaces such as space heaters, but a lot of the space heaters have the same parts. We want to focus today on furnaces that are directly tied into a HVAC system. The furnace components we will be discussing will most likely belong to your standard furnace that is tied into a duct system.
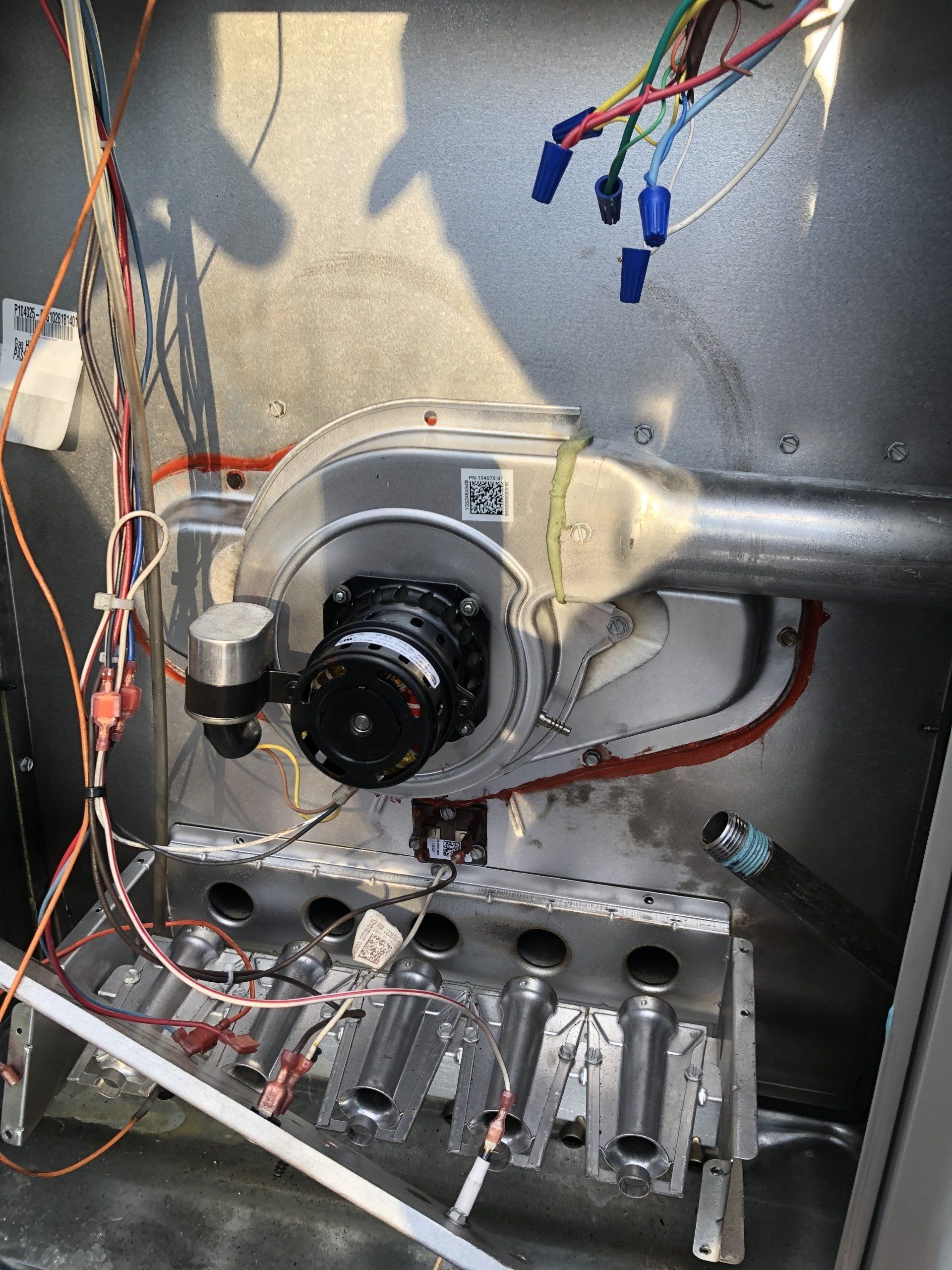

Heat Exchanger
When gas burns it gives off a very toxic chemical called carbon monoxide. When breathed in it it can be very detrimental to the health of the residents in the domicile. A heat exchanger will help prevent the toxic gas from mixing with fresh air. A heat exchanger is a relatively simple piece of equipment considering its job is so important. A heat exchanger has long metal tubes that have been bent into an S shape. Gas flames burn inside the tubes and expel the toxic gasses through the roof. The blower motor forces air on the outside of the tubes heating the air as it does. This also keeps toxic flame exhaust from mixing with the clean air. This component should be regularly checked for cracks due to its very important job. Carbon Monoxide detectors in your home are also very important. Checking your Carbon Monoxide detectors and your furnace regularly can ensure the safety of you and your family. For a better understanding we’ve listed the systematic process of a heat exchanger in a heating cycle below;
-
Burners trigger combustion gases and send them through the first opening in the heat exchanger.
-
At the same time as step one the blower releases cool air over the exterior of the heat exchanger.
-
It uses heated combustion gases to warm the air, which is then distributed throughout the home.
-
Toxic Exhaust is released through the roof exhaust or FLUE pipe.
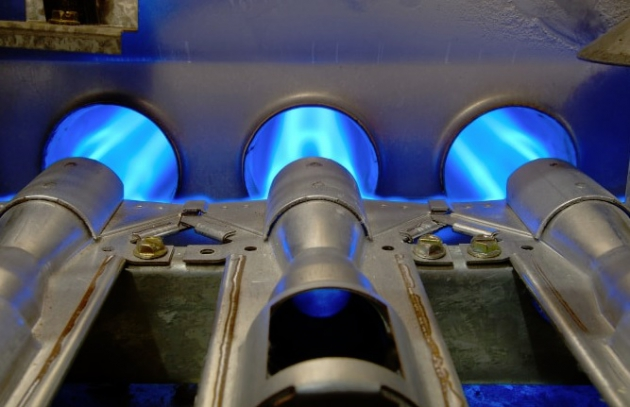

Igniter and Pilot Lights
A gas furnace needs some type of flame or very hot heat to initiate combustion. Older furnaces use a pilot light that burns constantly while the gas is on. Modern day furnaces use a Hot Surface Ignitor (HSI). The HSI (below) glows red hot, reaching a temperature hot enough to initiate the combustion process.

Burners
A burner is where gas and air are combined creating a flame that becomes the heat source.

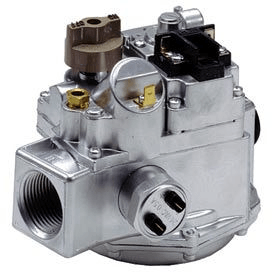
Gas Valve
Gasoline has to be pressurized when it enters your home from your gas line. The pressure is usually 8-12 inches of water column when it originally enters the home. The gas valve pressurizes it to the needed amount of pressure for the furnace which is usually 3-5 inches of water column. Inches of water column is used to measure gas pressure. The gas valve controls all the gas going into the furnace. When the safety switch fails the gas valve kind of acts like a secondary safety switch shutting down the pathway into which all gas to the furnace.
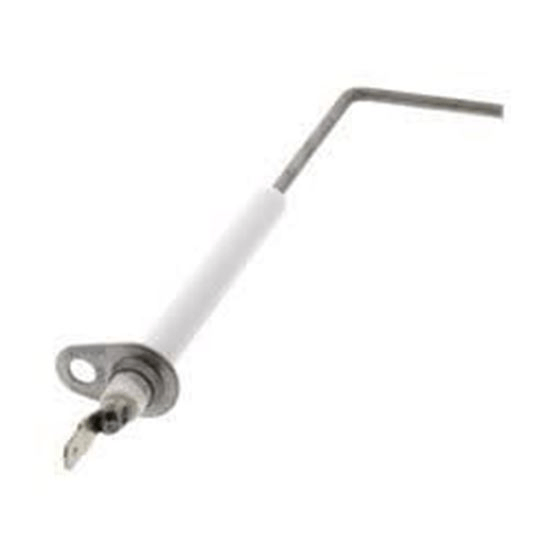
Thermocouple
A Thermocouple is used in relation to the pilot light to detect whether or not the pilot light is lit. It uses two small metal wires that rest inside a tube that when heated conduct electricity. After being heated they send a 24 volt signal to the gas valve allowing gas flow. If the thermocouple is bad or does not sense heat from the pilot light it will not allow gas into the system.

Flame Sensor
A flame sensor works as a safety to detect heat when a Hot Surface Igniter is used. If it does not detect heat it will shut off the gas.

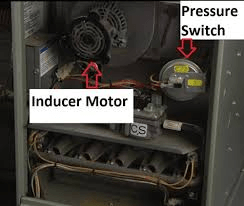
Draft Inducer Motor
Since when gas is burned it produces toxic fumes, it is necessary to have proper ventilation. This perhaps is one of the most important things that needs to happen in your furnace to ensure consumer safety. A draft inducer motor is triggered before the gas is. This in turn creates a vacuum inside the furnace system safely expelling combustion exhaust through the vent pipe.

Pressure Switch
The pressure switch’s job is to make sure the draft inducer motor has been turned on and is expelling gas properly through the vent. Inside is a small diaphragm that allows the switch to detect the vacuum that is pulled by the inducer motor. If a vacuum occurs then the diaphragm pulls in which activates a switch allowing gas flow. If a vacuum is not sensed then no gas will be allowed into the system.
Blower Motor
A blower motor is what blows the air into the vents of your home. The blower motor cycles air into the home from a return air filter past the heat exchanger and out into the home. Blower motors have a tendency to malfunction due to dirty air filters more than most components.

Blower Motor Capacitor
High and low voltage run through the capacitor run and send the necessary power to the blower motor. It is used to help start a blower motor and sometimes keep the blower motor running at a certain rate of speed in some cases. Not all systems use a capacitor to run the blower motor.

Furnace Limit Switch
A furnace has multiple safety switches contained within its system. Yet another is the furnace limit switch. When the furnace becomes too hot this switch is activated. The switch shuts off the gas to the system as soon as it’s activated. If at any point the the switch is triggered it will turn off all gas to the furnace until the problem is addressed.

Return Air Filter
The return air filter being dirty is one of the number one causes of dirt and debris entering your unit. To avoid this change out your filter every 30-60 days. This will prevent those debris from entering your system and keep your unit running for longer.

With all of your furnace needs this winter season allow us here at A-Plus Comfort LLC help you. We have over 5 years of experience in the HVAC trade in Huntsville, Alabama and the surrounding areas. We are more than happy to assist your in your HVAC needs or questions. Give us a call today at (256) 585-2550. Thank you!